#P10826. [EC Final 2020] Allin
[EC Final 2020] Allin
题目描述
(also known as , , and ) is one of the most popular variants of the card game of poker. $\textbf{Please read the following rules as they may be different from the regular rules.}$ cards, known as , are dealt to each player. Each player only knows his own hole cards. And then are dealt in three stages . The stages consist of a series of three cards (the flop), later an additional single card (the turn or fourth street), and a final card (the river or fifth street). All players know the face-up cards that are already dealt. All cards are drawn from a standard 52-card deck. A standard 52-card deck comprises ranks in each of the four French suits: clubs (), diamonds (), hearts () and spades (). Each suit includes an Ace (A), a King (K), Queen (Q) and Jack (J), each depicted alongside a symbol of its suit; and numerals or pip cards from the Deuce (Two) to the Ten, with each card depicting that many symbols (pips) of its suit.
Individual cards are ranked as follows (high-to-low): A, K, Q, J, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2. $\textbf{Each player seeks the best five-card poker hand from any combination of the seven cards}$ -- $\textbf{the five community cards and his two hole cards}.$
The following table shows the possible five-card poker hand types in of their values. Each type has a specific ordering of the five cards that is described below. $\textbf{The following part is describing how to compare two hands}$,
- : Simple value of the card. The cards are ordered as such that . ( represents the rank of -th card.)
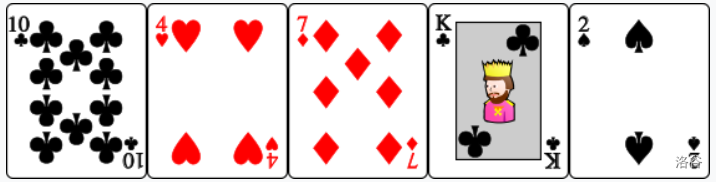
- : Two cards with the same value. The cards are ordered as such that , , , , .
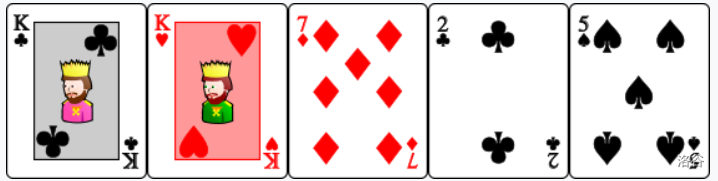
- : Two times two cards with the same value. The cards are ordered as such that , , , , .
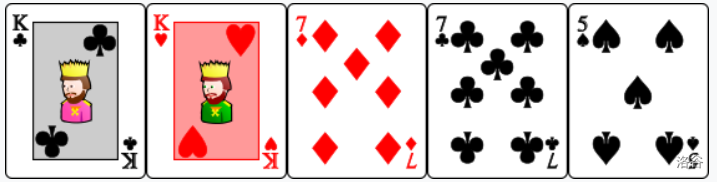
- : Three cards with the same value. The cards are ordered as such that ,, , .
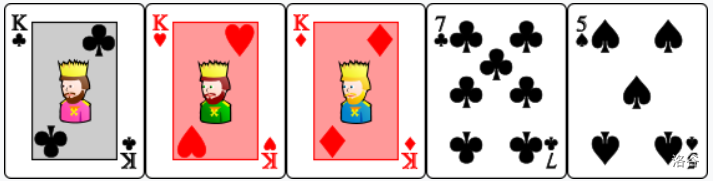
- : Sequence of 5 cards in increasing value. The cards are ordered as such that is exactly one rank above for all . $\textbf{can be 2. In this case, Ace is considered one rank below 2.}$
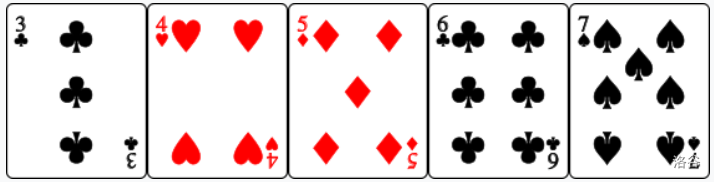
- : 5 cards of the same suit. The cards are ordered as such that all the five cards have the same suit and .
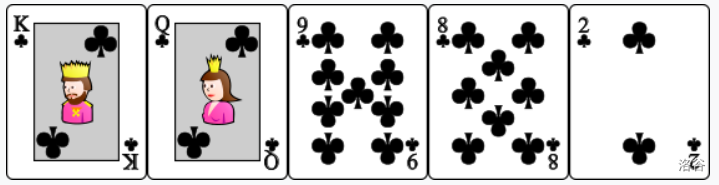
- : Combination of three of a kind and a pair. The cards are ordered as such that , .
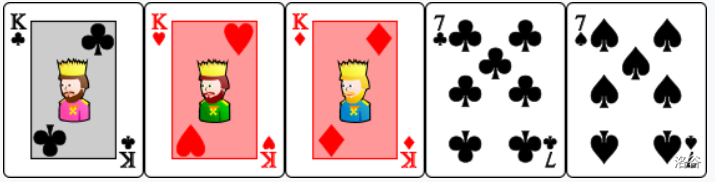
- : Four cards of the same value. The cards are ordered as such that .
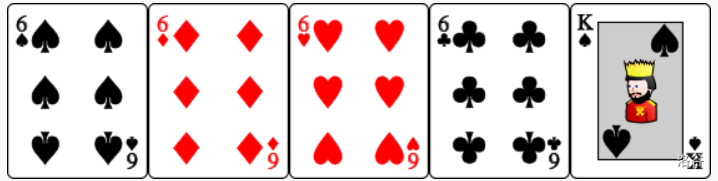
- : Straight of the same suit. The cards are ordered as such that all the five cards have the same suit and that is exactly one rank above for all . $\textbf{can be 2. In this case, Ace is considered one rank below 2.}$
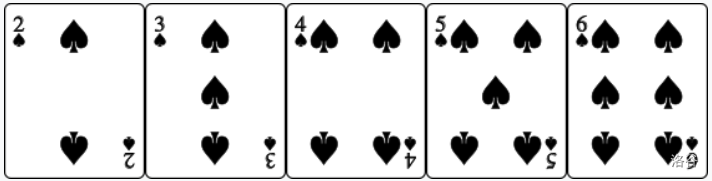
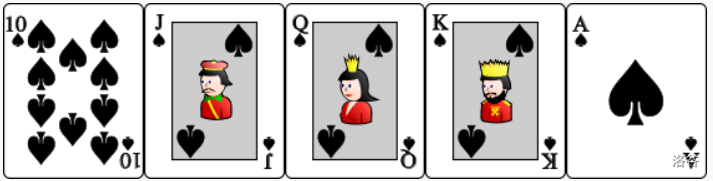
- : Straight flush from Ten to Ace. The cards are ordered as such that are Ace, King, Queen, Jack, Ten of the same suit.
To compare two hands, first, we will compare the type of two hands. For example, one hand is , the other hand is , always win .
If the types of two hands are the same, we compare the ranks of the cards. We will order the card as described above, and compare them one by one. Firstly, we will compare the first card. If a hand's first card has a higher rank, it wins. If the first cards of the two hands have the same rank, we will compare the second card, and so on. If the cards have the same rank in every position, no one wins. The suit of cards never matters. For example, 5, 5, 5, 2, 2 can win 3, 3, 3, A, A. Since they are both , and we will compare the ranks of the three cards of a kind at first.
Consider the case that the hole cards of Alice are A, 4 and the hole cards of Bob are 2, 3. The community cards are A, 4, 5, Q, Q. The best hand of Alice (five cards among her hole cards and the community hards) is A, A, Q, Q, 5, which is . The best hand of Bob is 5, 4, 3, 2, A, which is . Thus, Bob wins.
Players have betting options to check, call, raise, or fold. $\textbf{In this problem, we do not care about the meanings of these bets.}$ Rounds of betting take place before the flop is dealt and after each subsequent deal. The player who has the best hand and has not folded by the end of all betting rounds wins all of the money bet for the hand, known as the pot. In certain situations, a split-pot or tie can occur when two players have hands of equivalent value. This is also called a chop-pot. $\textbf{In this problem, we assume the two players never fold.}$ So the player with the best five-card poker hand from any combination of the seven cards wins. If the two players have hands of equal values, no one wins.
To simplify the statement, we do not introduce the detailed rules here.
Daddy Dream is a world-famous player. As a strong challenger, Wolf Chicken wants to beat Daddy Dream. Wolf Chicken plays first after the flop (three cards are dealt face-up). Both players know the three face-up cards and each player knows his own two hole cards. Wolf Chicken will choose to allin if and only if he will certainly win whatever the the turn, the river (the remaining two community cards that have not been revealed) and Daddy Dream's hole cards are. Otherwise, Wolf Chicken will choose to check.
Given Wolf Chicken's two hole cards and the three flop cards, help him to determine whether he can allin.
输入格式
The first line contains a single integer () denoting the number of test cases.
For each test case, there is one line containing five strings separated by single spaces denoting the first hole card, the second hole card, the first community card, the second community card and the third community card.
For each card, the first character of its corresponding string denotes its rank. (Possible ranks are 2 ,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,T,J,Q,K,A. T denotes .) The second character denotes its suit. C denotes clubs. D denotes diamonds. H denotes hearts. S denotes spades.
It is guaranteed that each card appears at most once in one test case.
输出格式
For each test case, print one line. Print if Wolf Chicken will certainly win. Otherwise, print .
2
AC KC QC JC TC
AC TD 8S 5H 2C
allin
check
